Het arrangement Sleeping and dreaming - hv3 is gemaakt met Wikiwijs van Kennisnet. Wikiwijs is hét onderwijsplatform waar je leermiddelen zoekt, maakt en deelt.
- Auteur
- Laatst gewijzigd
- 11-05-2025 19:46:39
- Licentie
-
Dit lesmateriaal is gepubliceerd onder de Creative Commons Naamsvermelding-GelijkDelen 4.0 Internationale licentie. Dit houdt in dat je onder de voorwaarde van naamsvermelding en publicatie onder dezelfde licentie vrij bent om:
- het werk te delen - te kopiëren, te verspreiden en door te geven via elk medium of bestandsformaat
- het werk te bewerken - te remixen, te veranderen en afgeleide werken te maken
- voor alle doeleinden, inclusief commerciële doeleinden.
Meer informatie over de CC Naamsvermelding-GelijkDelen 4.0 Internationale licentie.
Aanvullende informatie over dit lesmateriaal
Van dit lesmateriaal is de volgende aanvullende informatie beschikbaar:
- Toelichting
- Deze les valt onder de arrangeerbare leerlijn van de Stercollectie voor Engels voor havo en vwo, leerjaar 3. Dit is thema 8 'Dreams'. Het onderwerp van deze les is: Sleeping and dreaming. Deze les staat in het teken van slapen en dromen. Hierbij wordt bijvoorbeeld de hoeveelheid slaap besproken en (nare) dromen. De onregelmatige werkwoorden in deze les zijn: to sweep, to swim, to take en to teach. In de grammaticaopdracht wordt de 'the zero conditional' behandeld.
- Leerniveau
- HAVO 3; VWO 3;
- Leerinhoud en doelen
- Engels;
- Eindgebruiker
- leerling/student
- Moeilijkheidsgraad
- gemiddeld
- Studiebelasting
- 1 uur 40 minuten
- Trefwoorden
- arrangeerbaar, dromen, dromen verklaren, engels, leerlijn, rearrangeerbare, slapen, stercollectie, the zero conditional
Gebruikte Wikiwijs Arrangementen
VO-content Engels. (z.d.).
BLOKKEN TEMPLATE - hv123
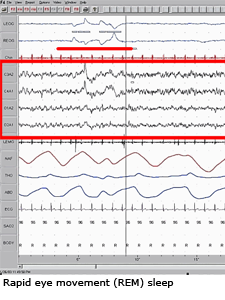
 The subject of this double period is sleeping and dreaming.
The subject of this double period is sleeping and dreaming.