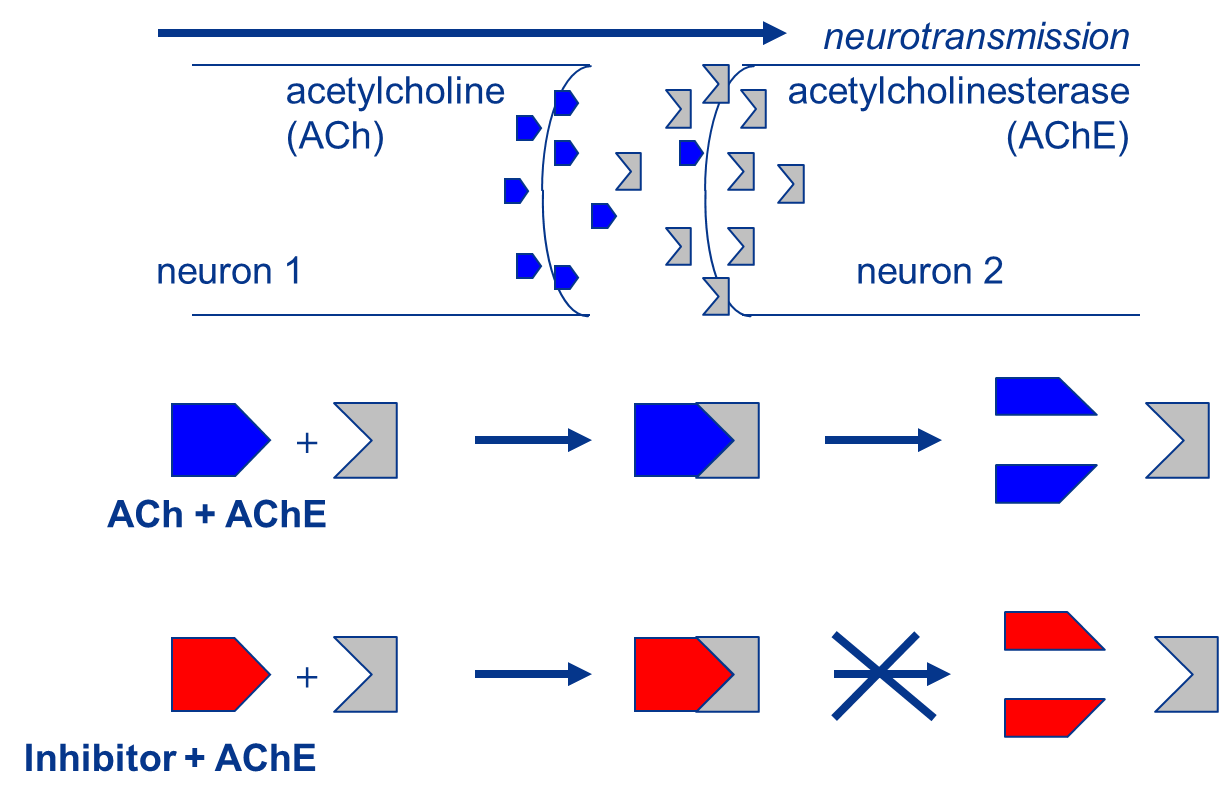
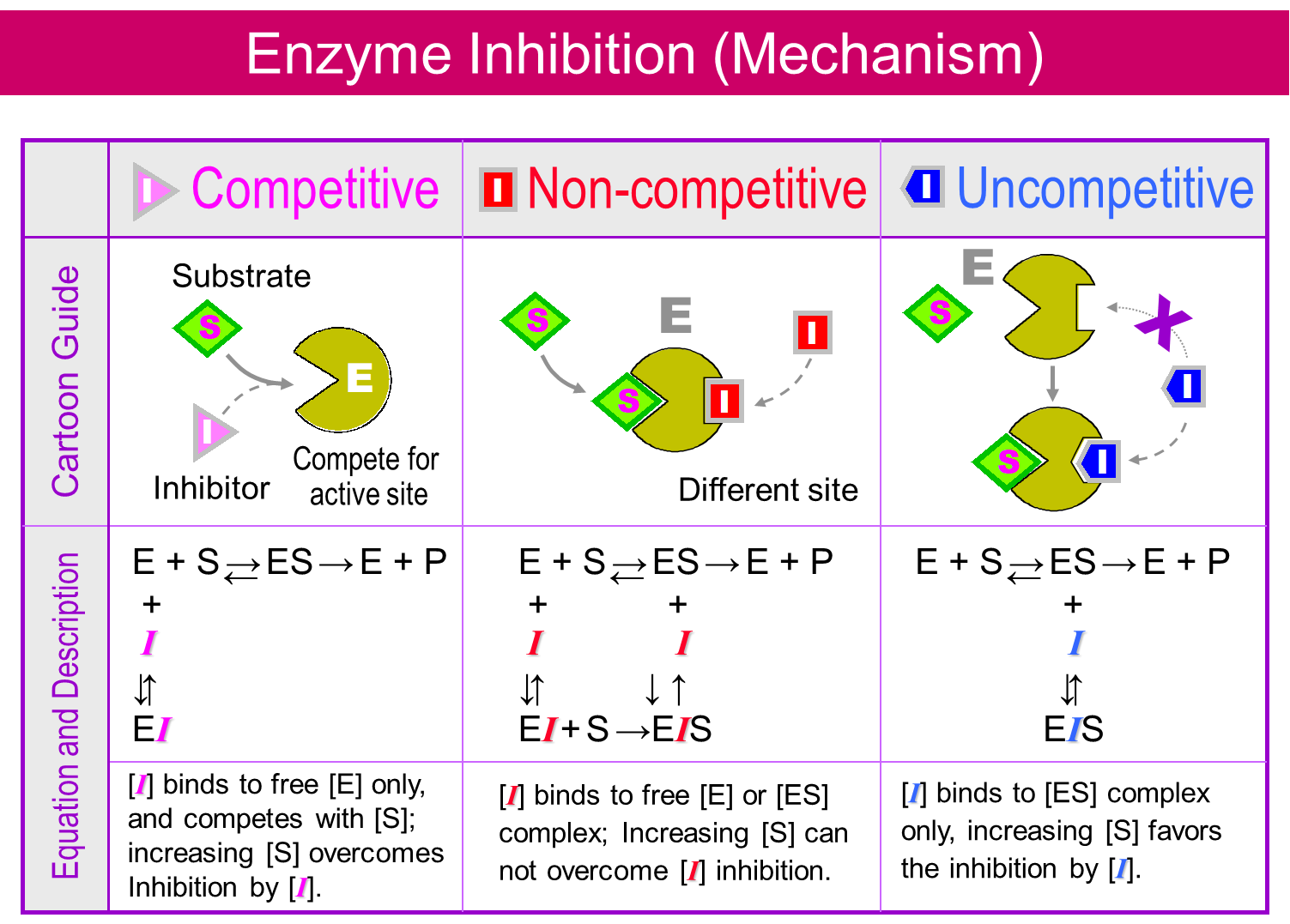
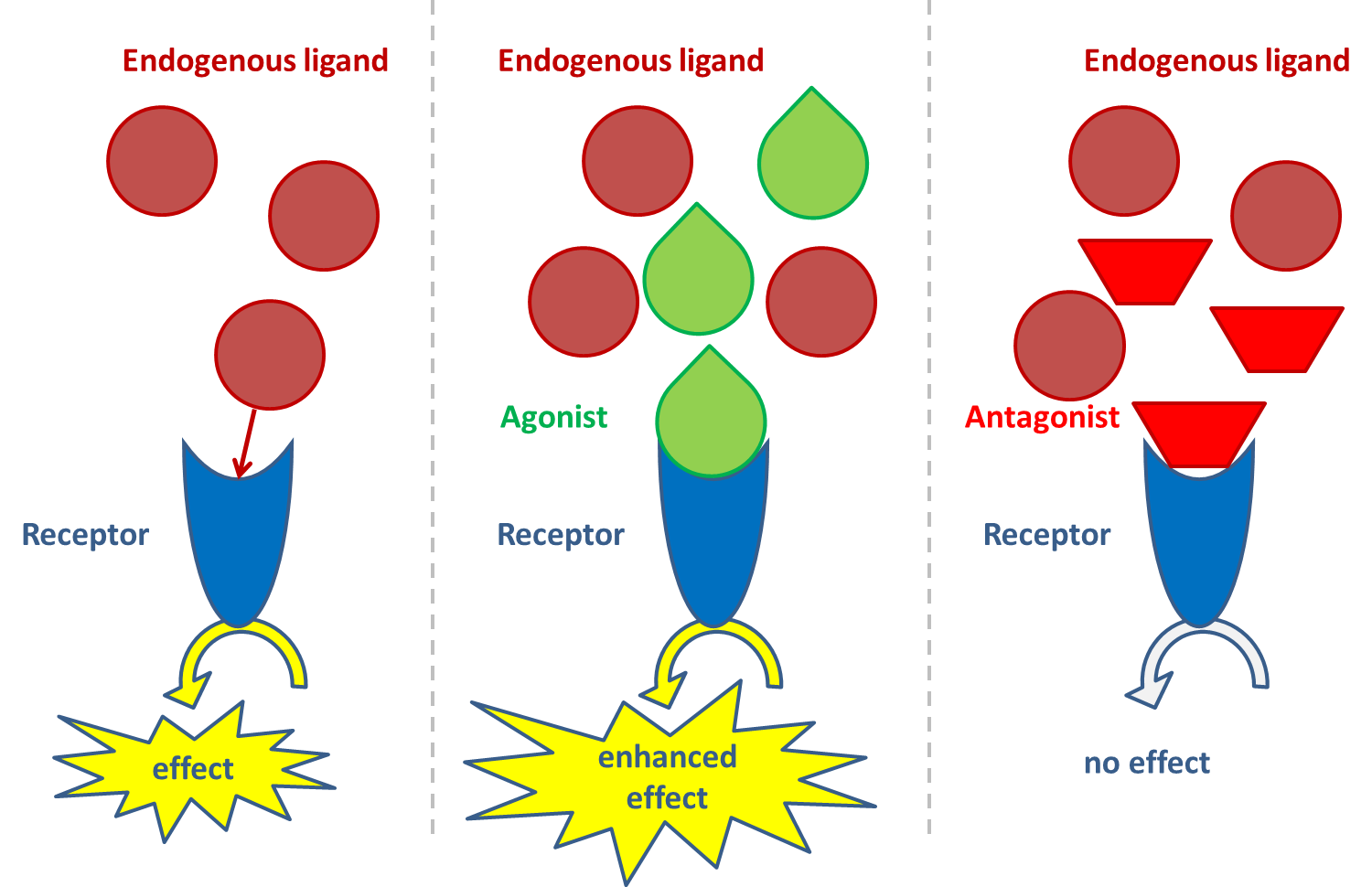
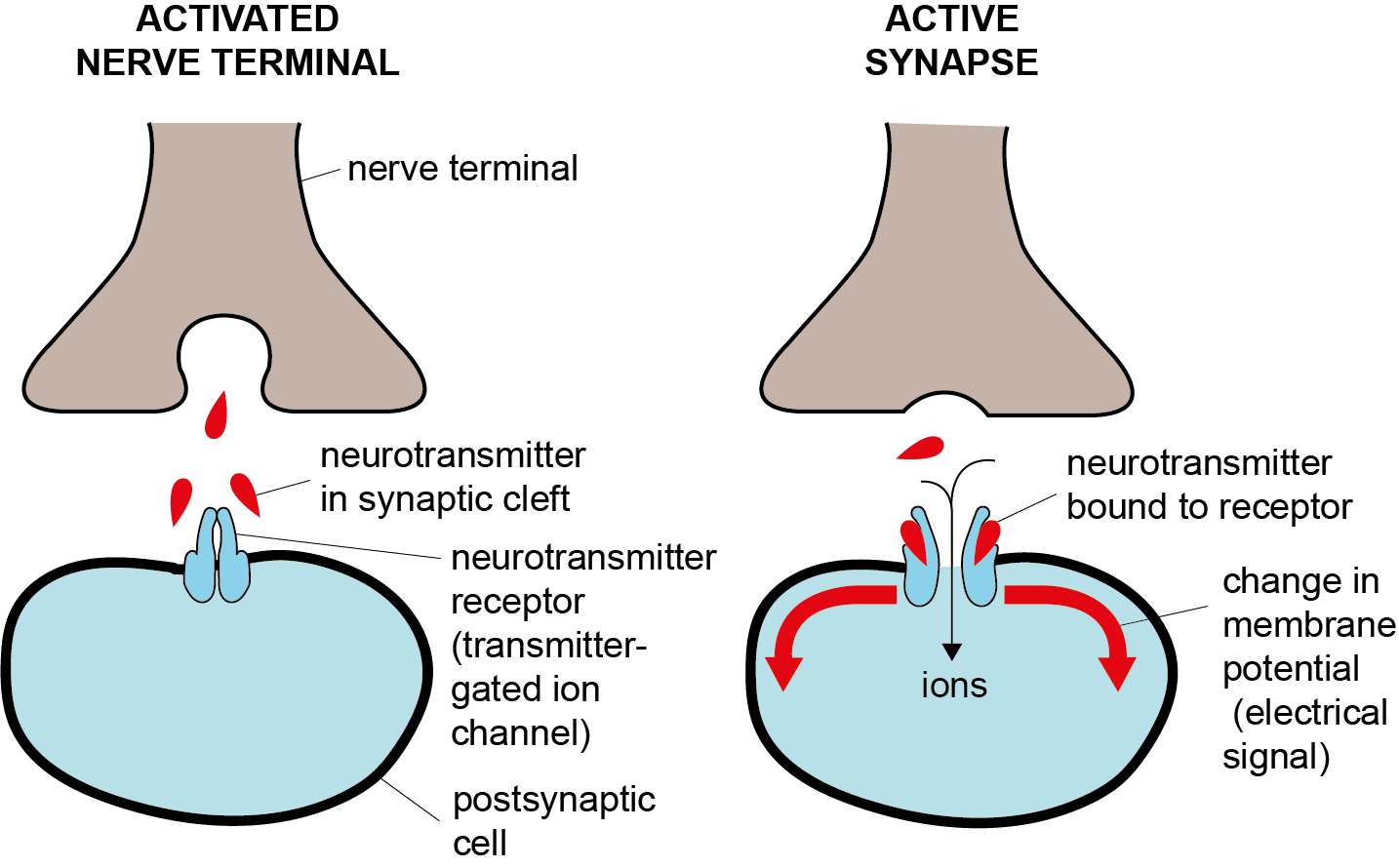
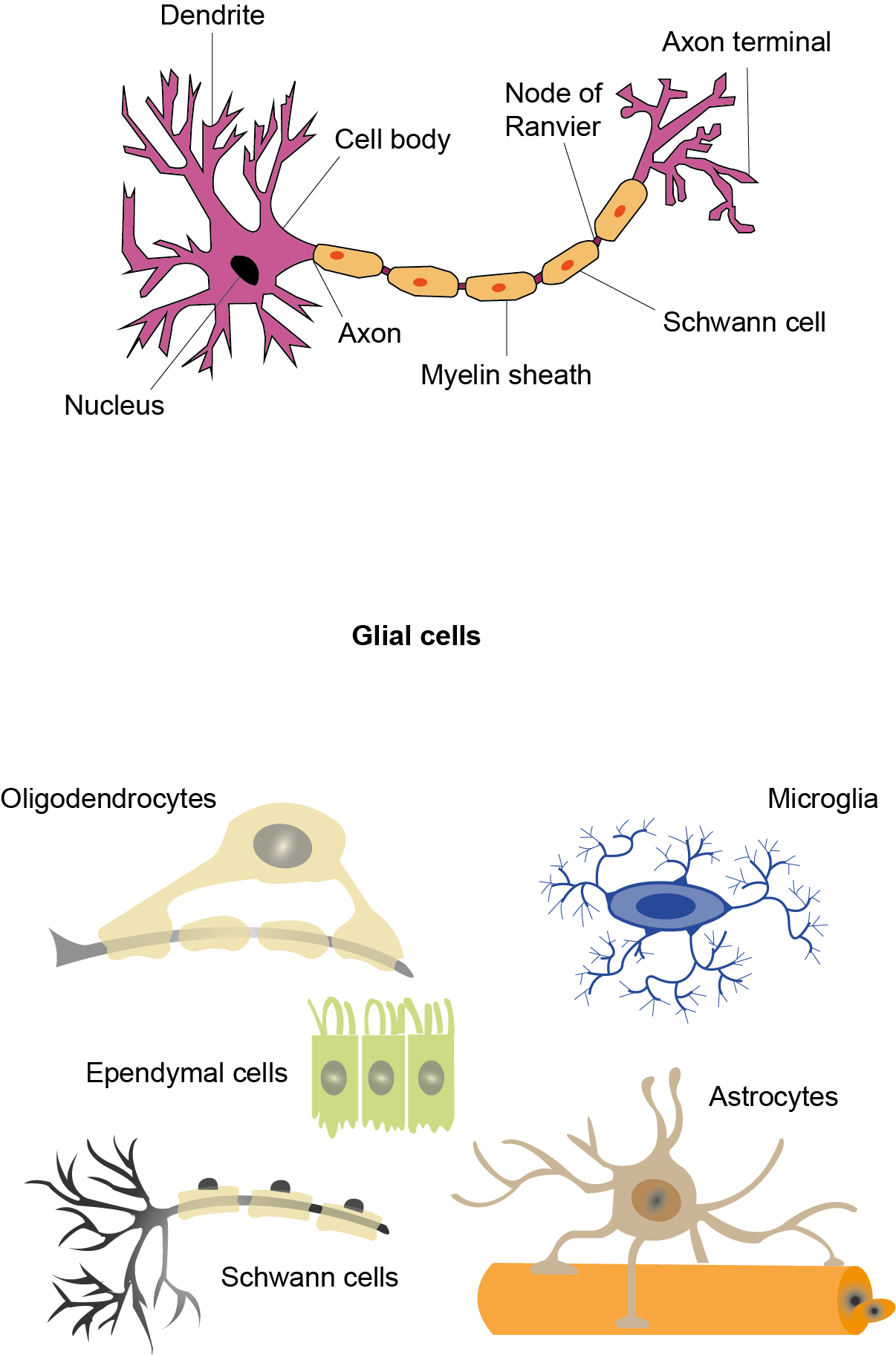
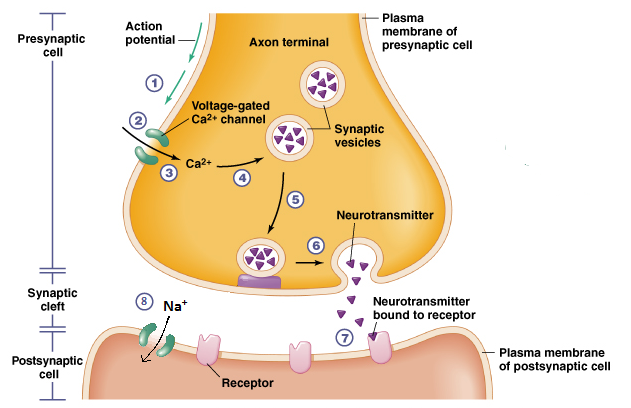
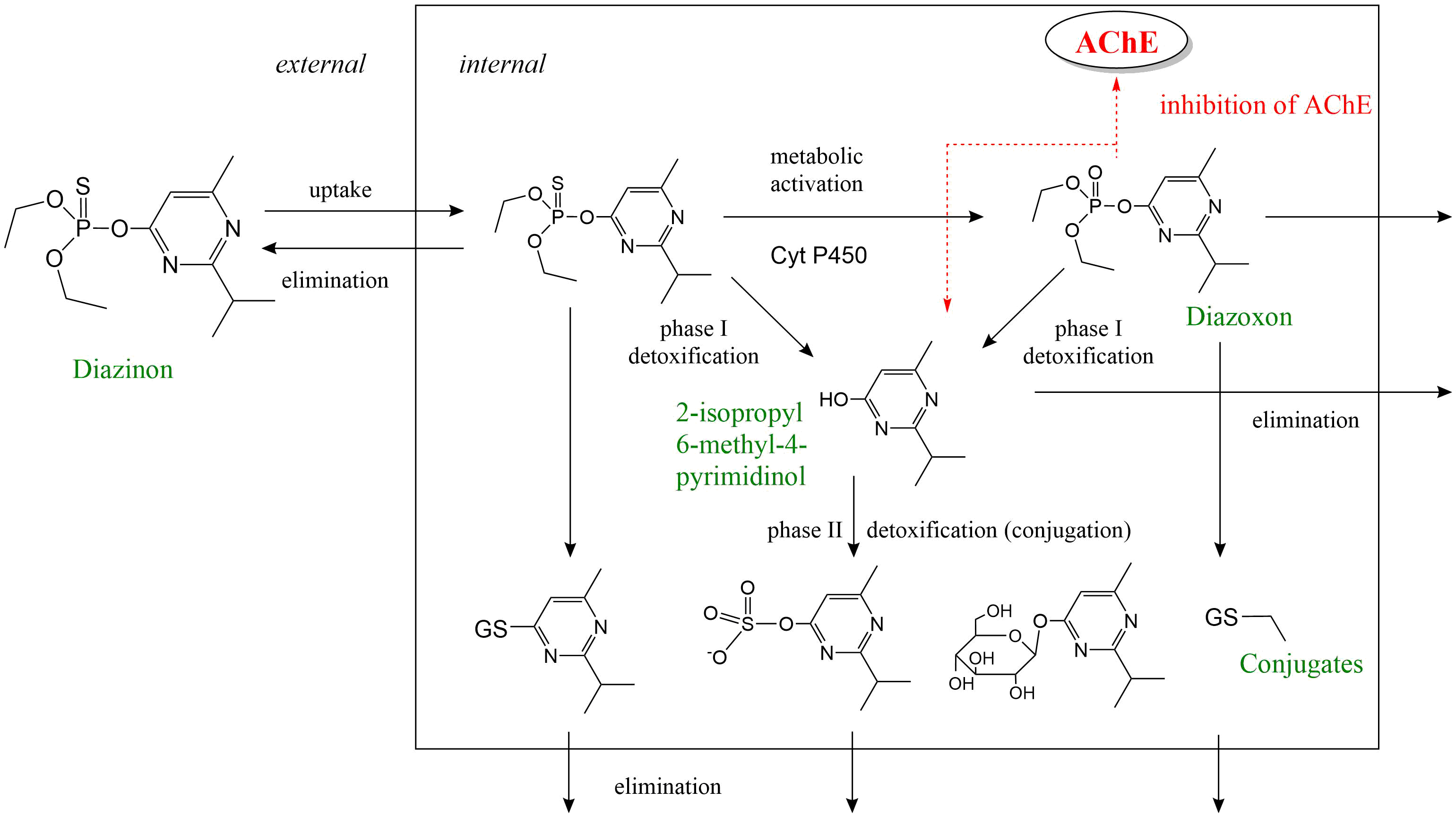
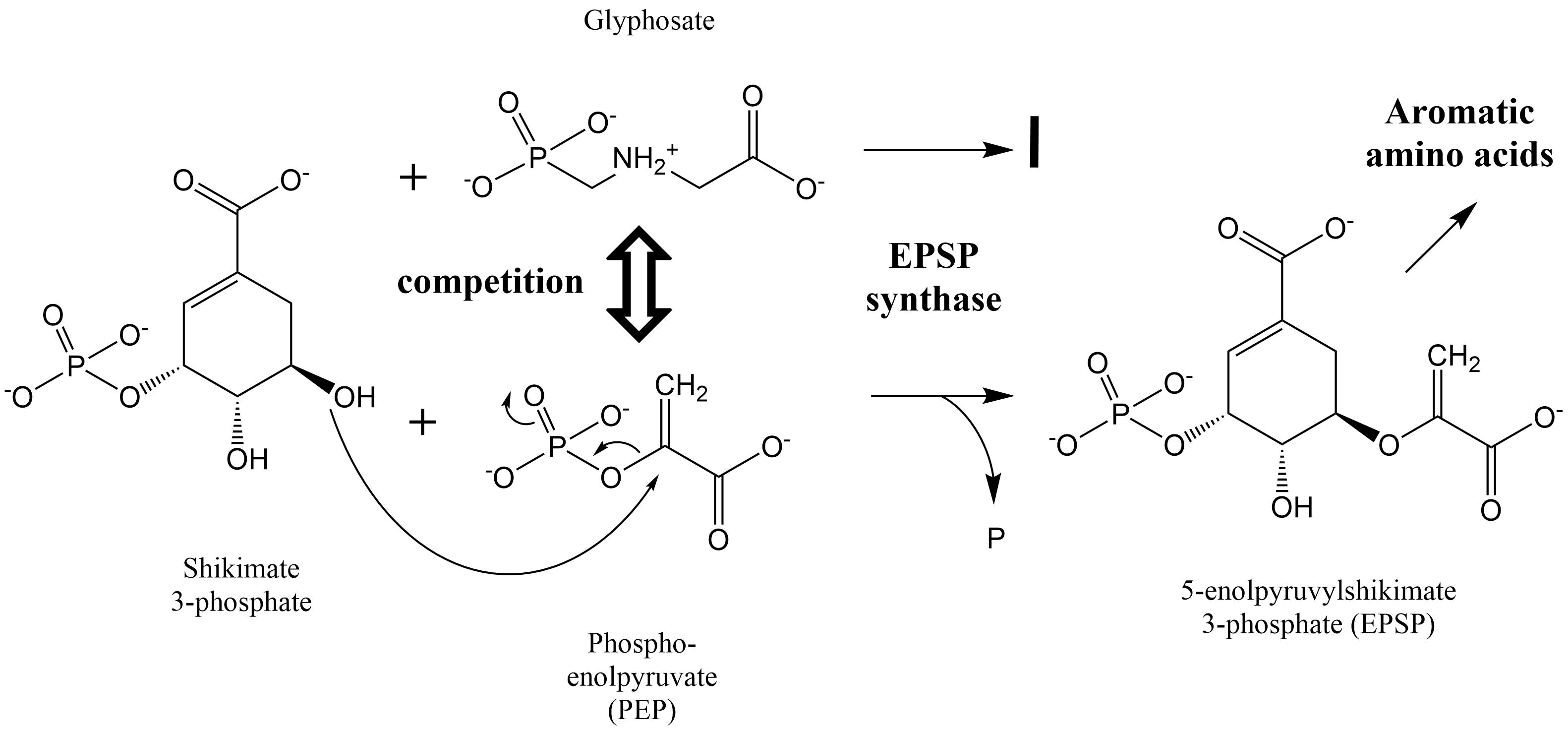
Het arrangement 4. Toxicology is gemaakt met Wikiwijs van Kennisnet. Wikiwijs is hét onderwijsplatform waar je leermiddelen zoekt, maakt en deelt.
- Auteur
- Laatst gewijzigd
- 10-01-2023 09:52:21
- Licentie
-
Dit lesmateriaal is gepubliceerd onder de Creative Commons Naamsvermelding 4.0 Internationale licentie. Dit houdt in dat je onder de voorwaarde van naamsvermelding vrij bent om:
- het werk te delen - te kopiëren, te verspreiden en door te geven via elk medium of bestandsformaat
- het werk te bewerken - te remixen, te veranderen en afgeleide werken te maken
- voor alle doeleinden, inclusief commerciële doeleinden.
Meer informatie over de CC Naamsvermelding 4.0 Internationale licentie.
Aanvullende informatie over dit lesmateriaal
Van dit lesmateriaal is de volgende aanvullende informatie beschikbaar:
- Eindgebruiker
- leerling/student
- Moeilijkheidsgraad
- gemiddeld
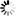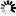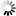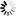

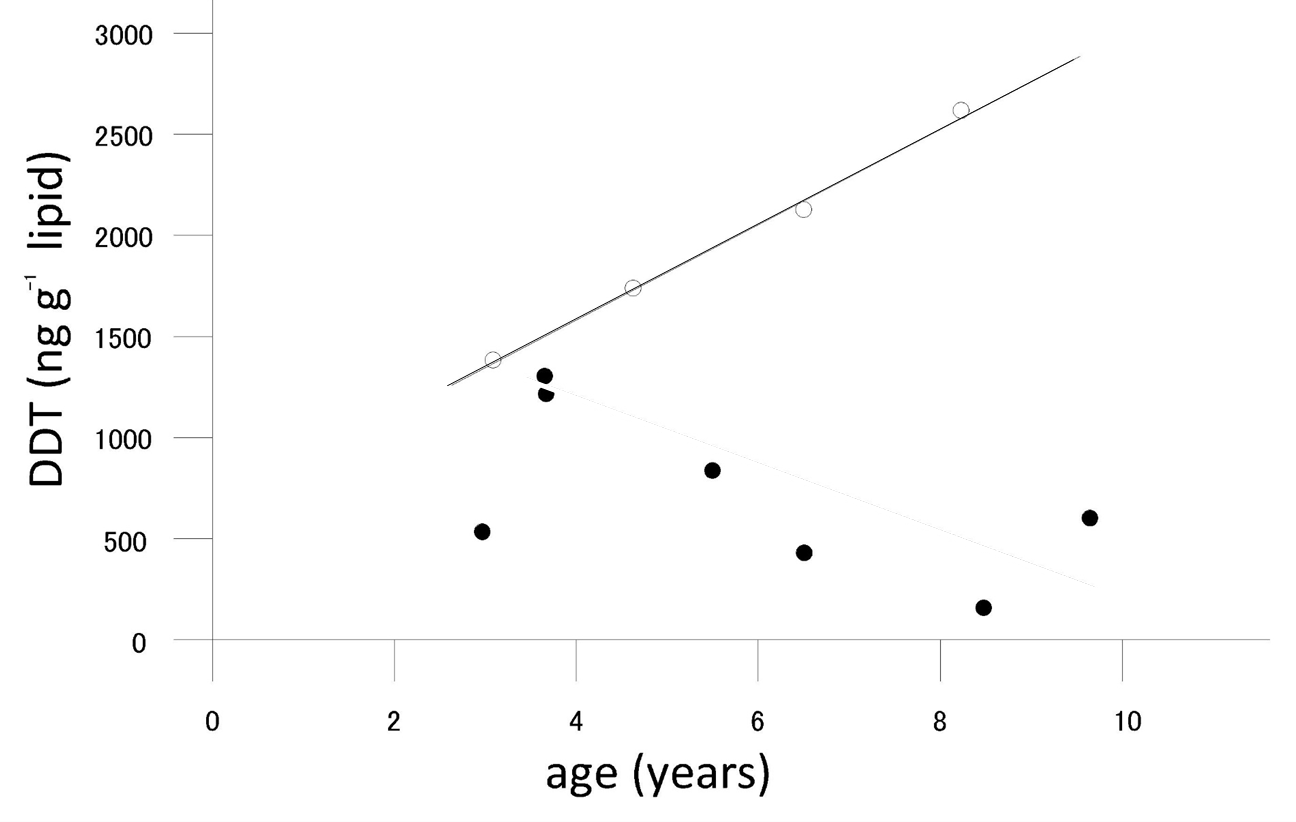
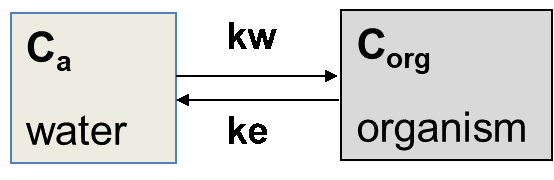
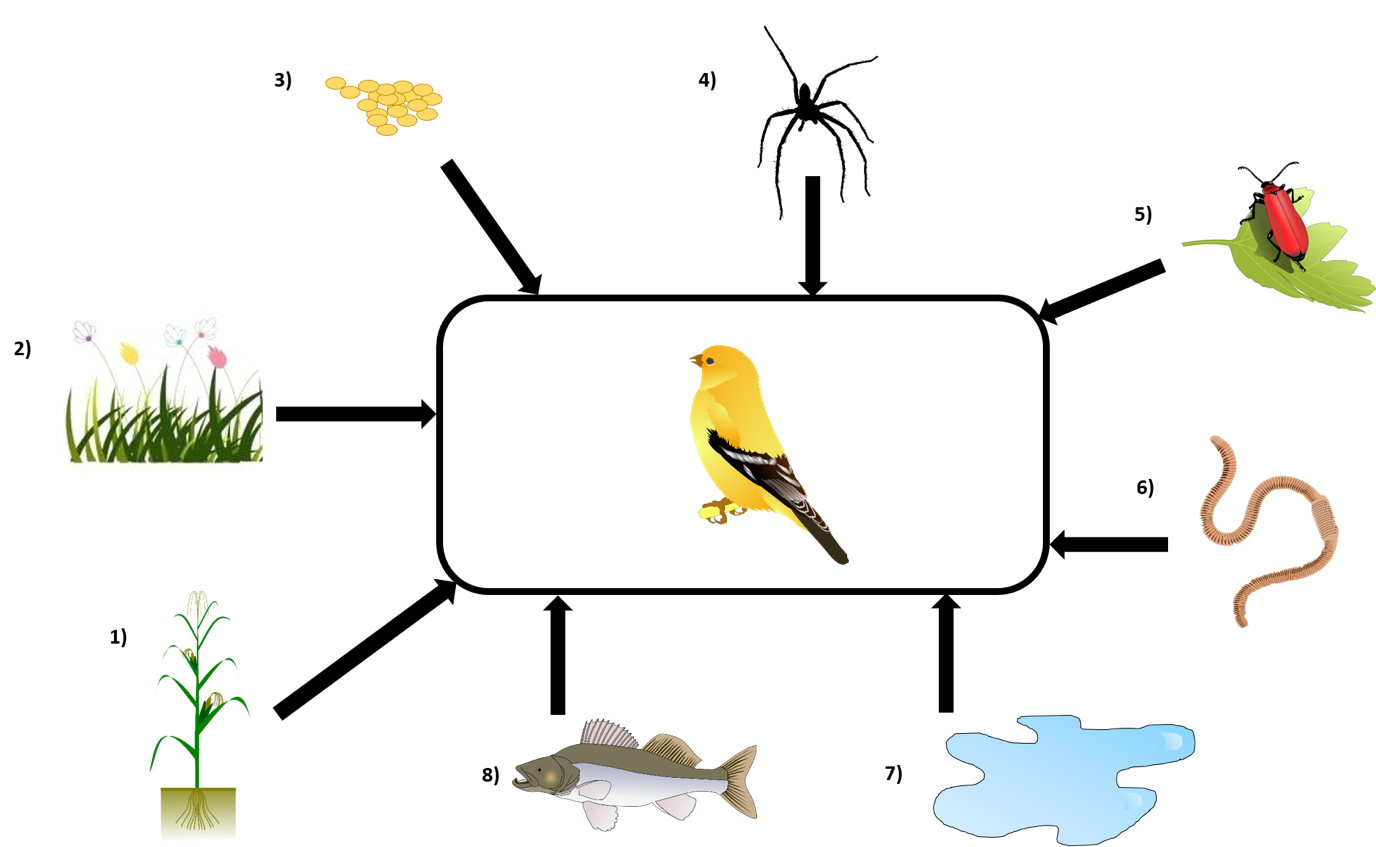
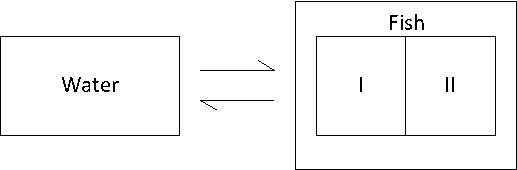
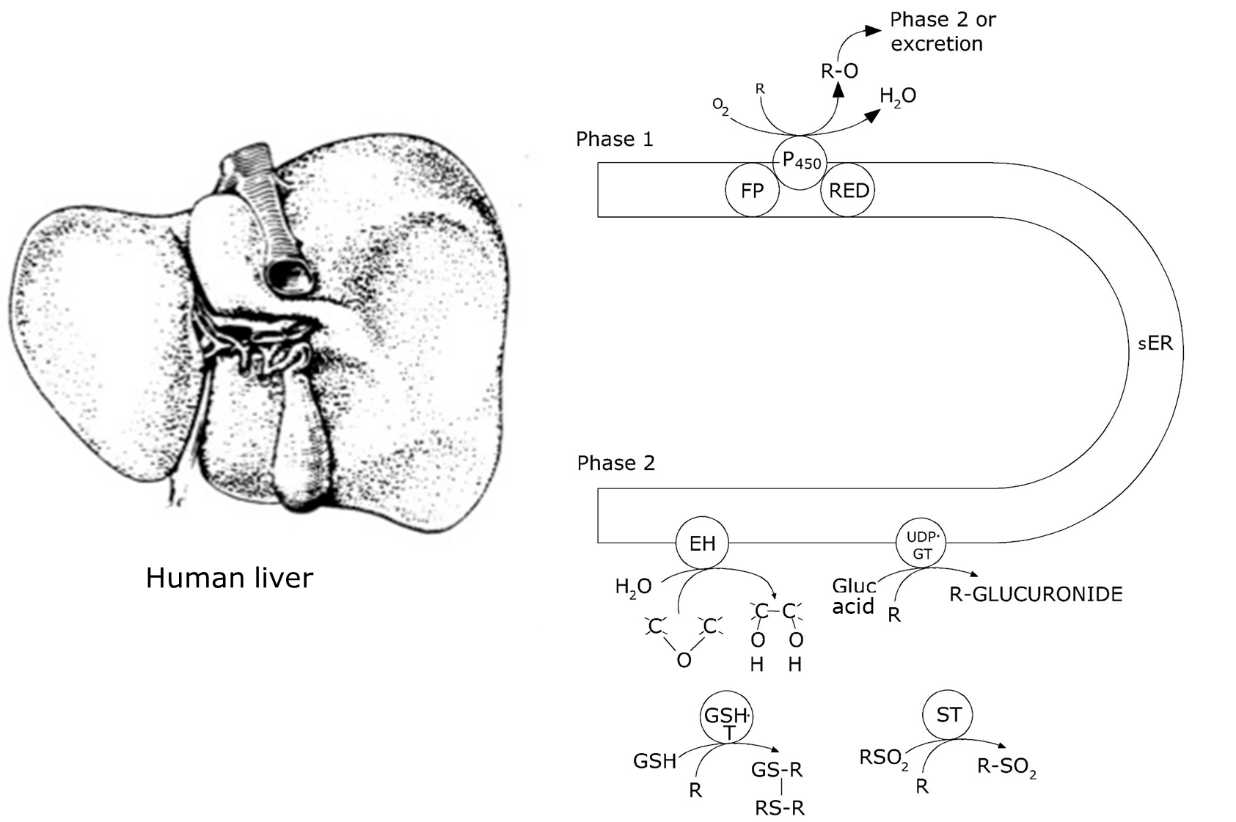
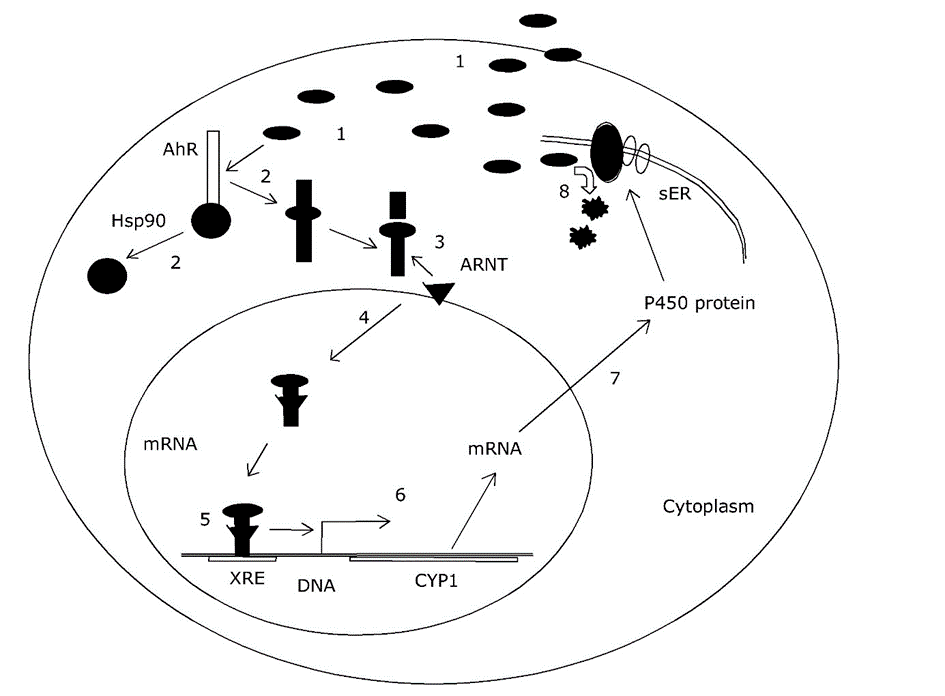
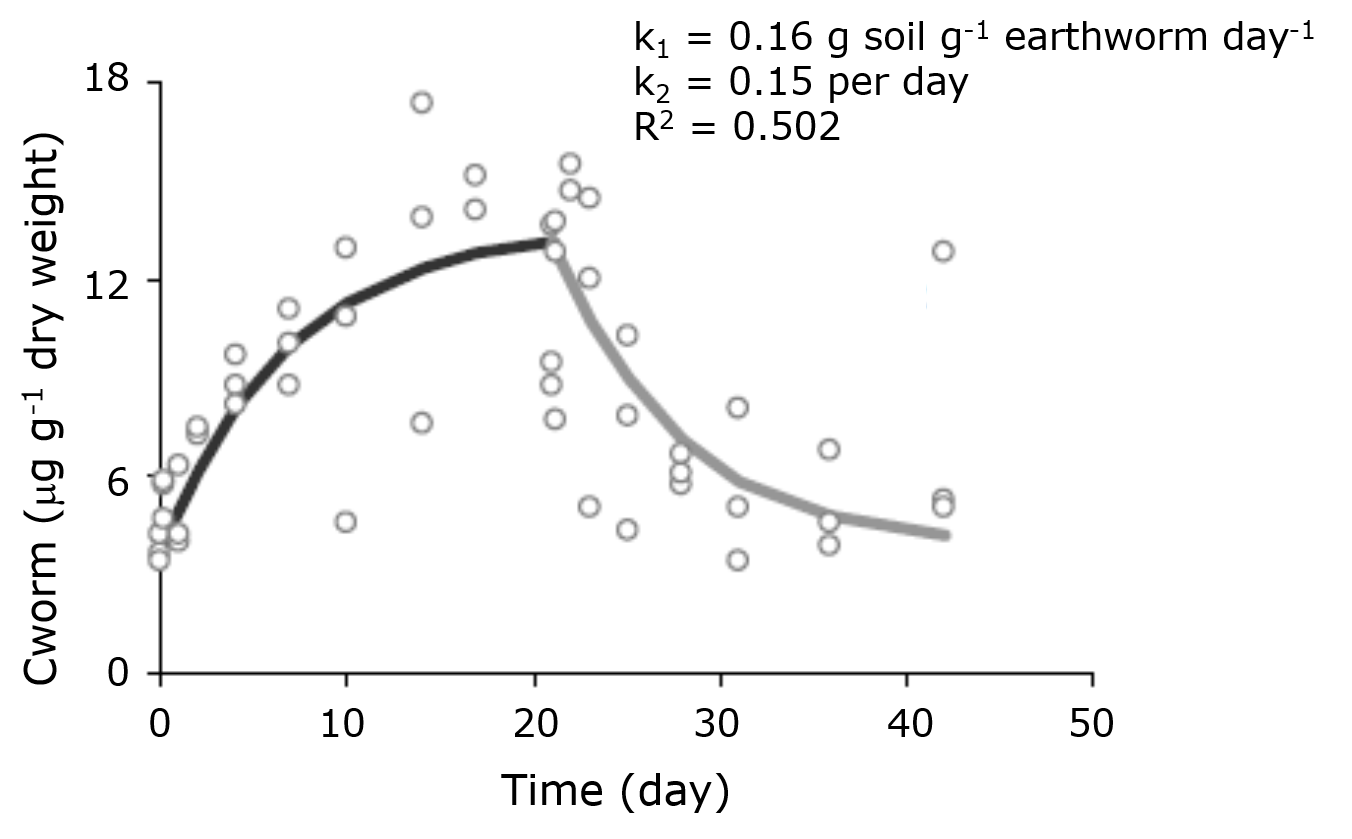
 is the uptake rate constant and k2 the elimination rate constant, both with dimension time-1. However, it is often more practical to work with the concentration in the animal (e.g. expressed in mg/kg). This can be achieved by dividing the left and right sides of the equation by w, the body-weight of the animal and defining Cint = Q/w. In addition, we define the external concentration as Cenv = F/V, where V is the volume (L or kg) of the environmental compartment. This leads to the following formulation of the differential equation:
is the uptake rate constant and k2 the elimination rate constant, both with dimension time-1. However, it is often more practical to work with the concentration in the animal (e.g. expressed in mg/kg). This can be achieved by dividing the left and right sides of the equation by w, the body-weight of the animal and defining Cint = Q/w. In addition, we define the external concentration as Cenv = F/V, where V is the volume (L or kg) of the environmental compartment. This leads to the following formulation of the differential equation:
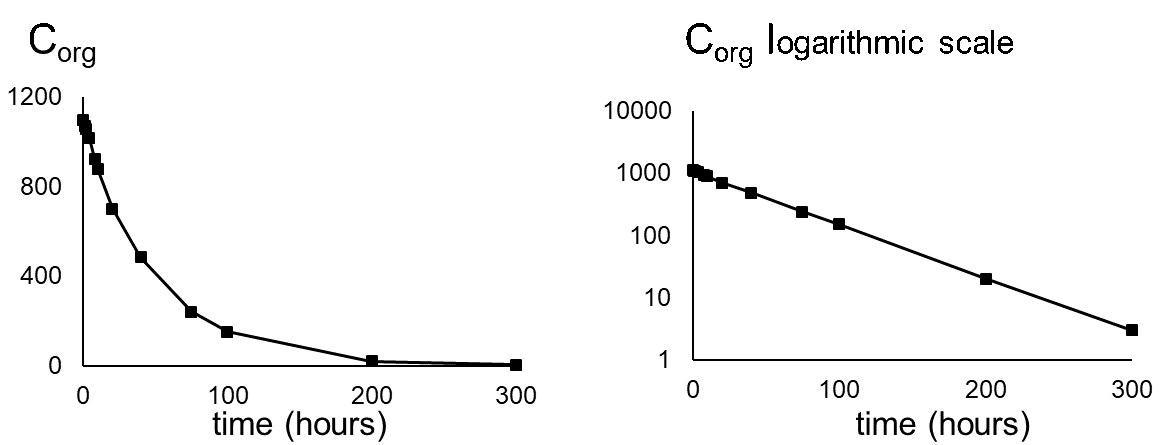
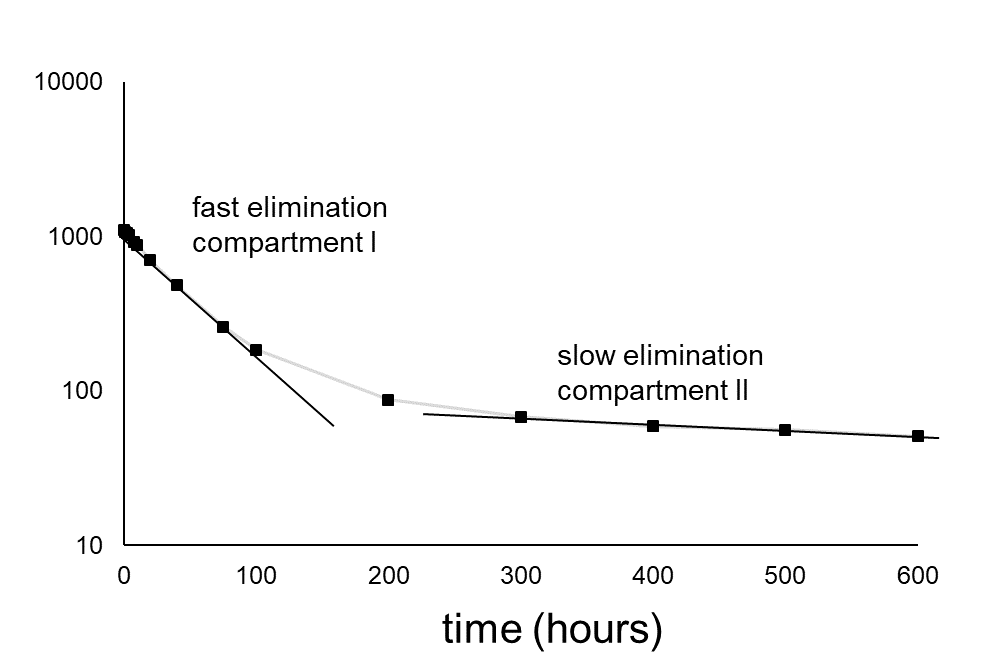
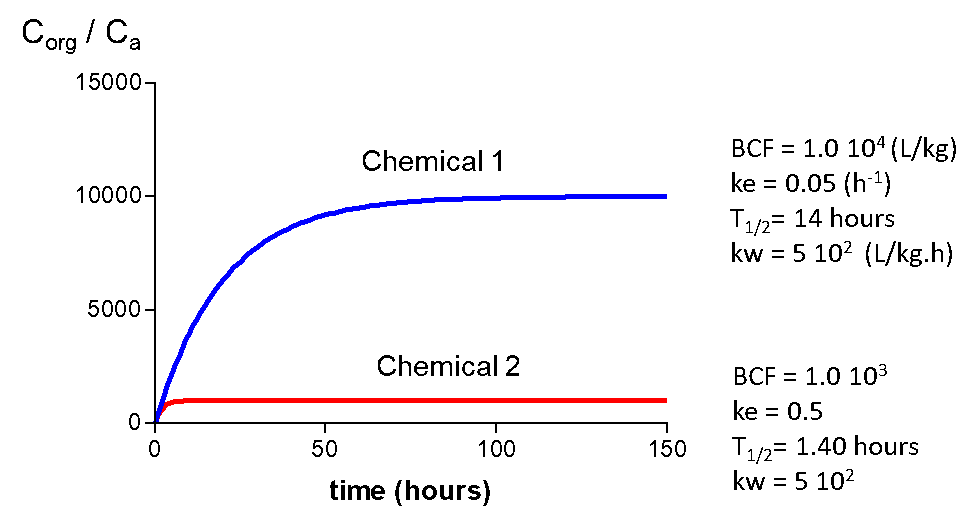
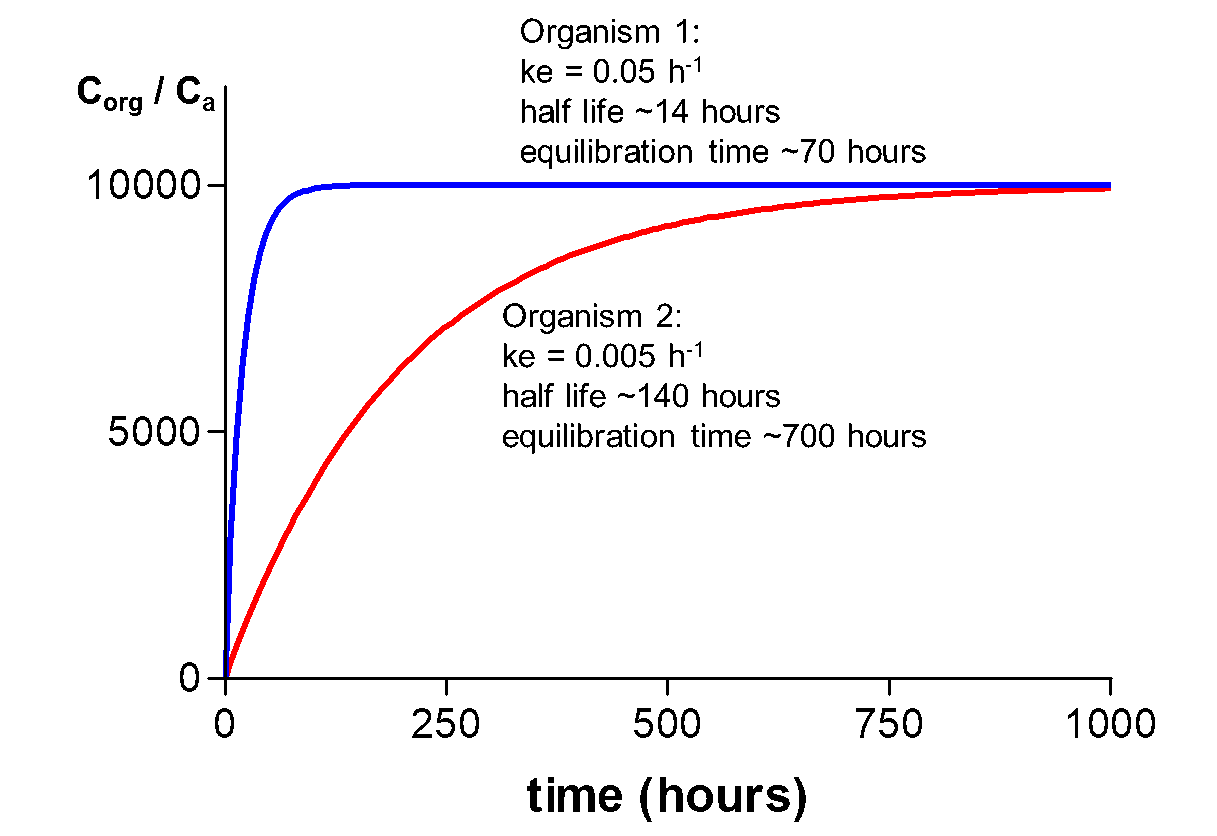
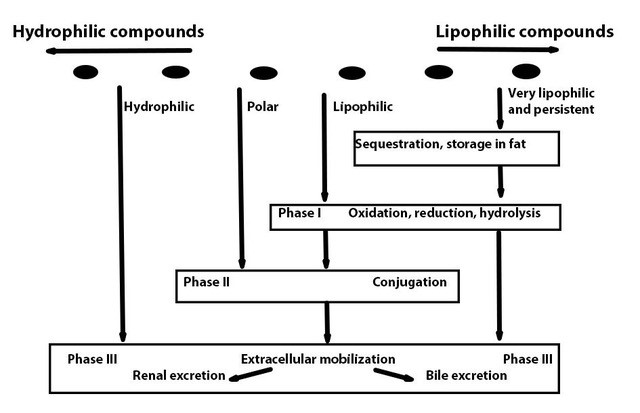
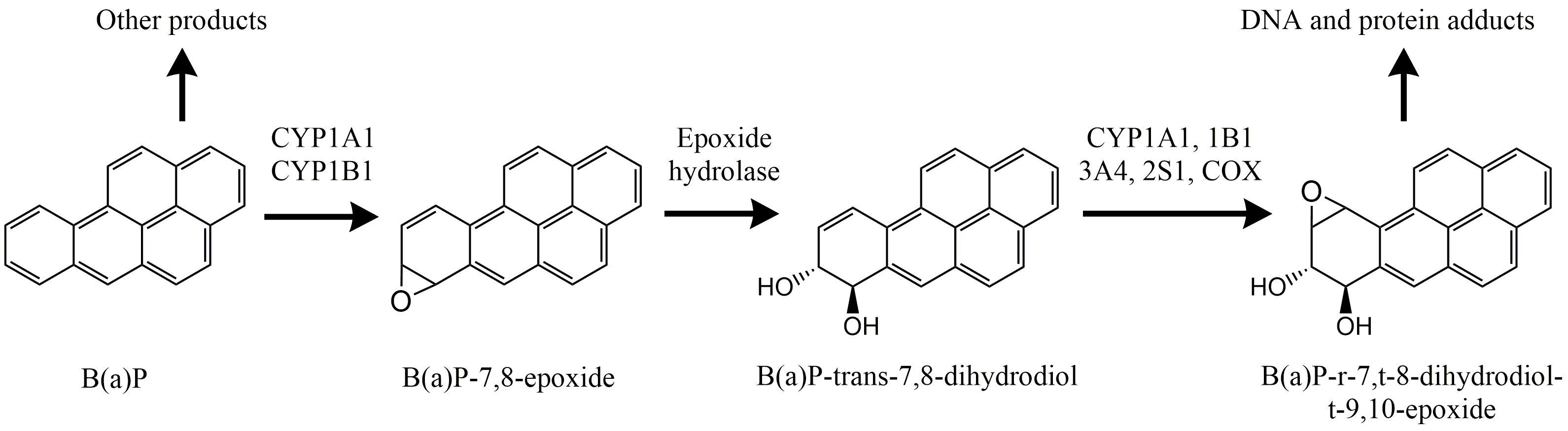
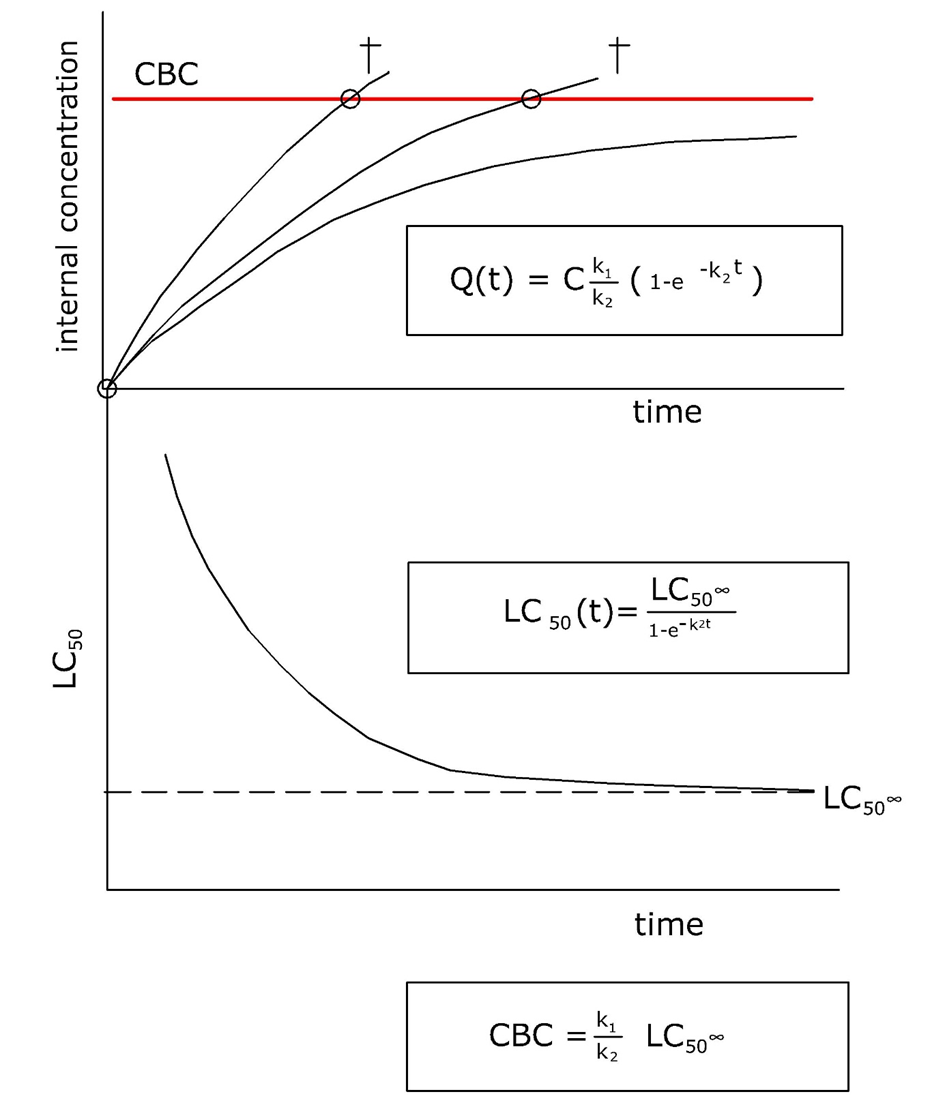
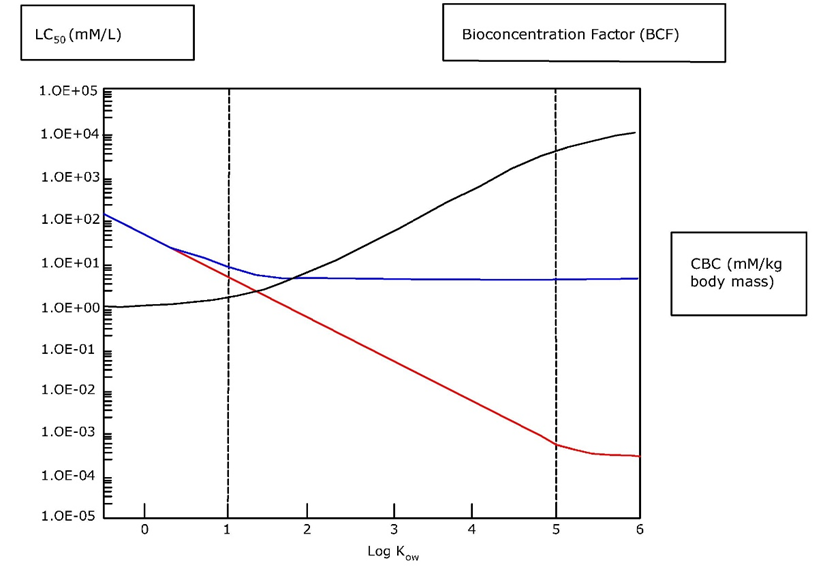
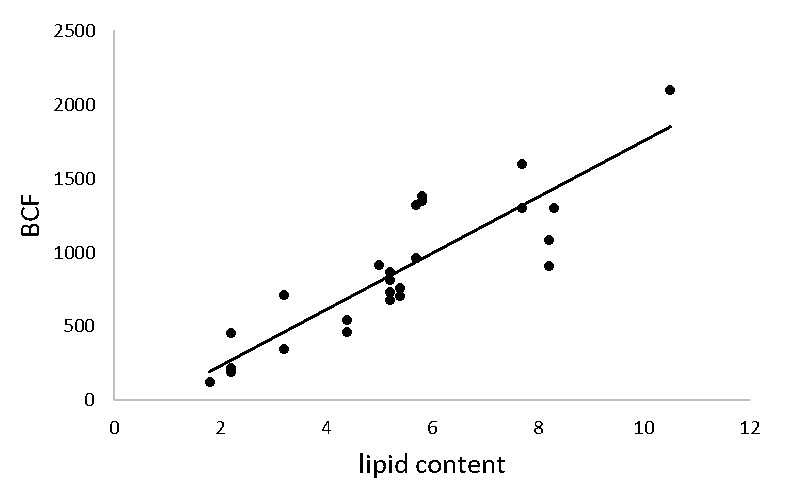
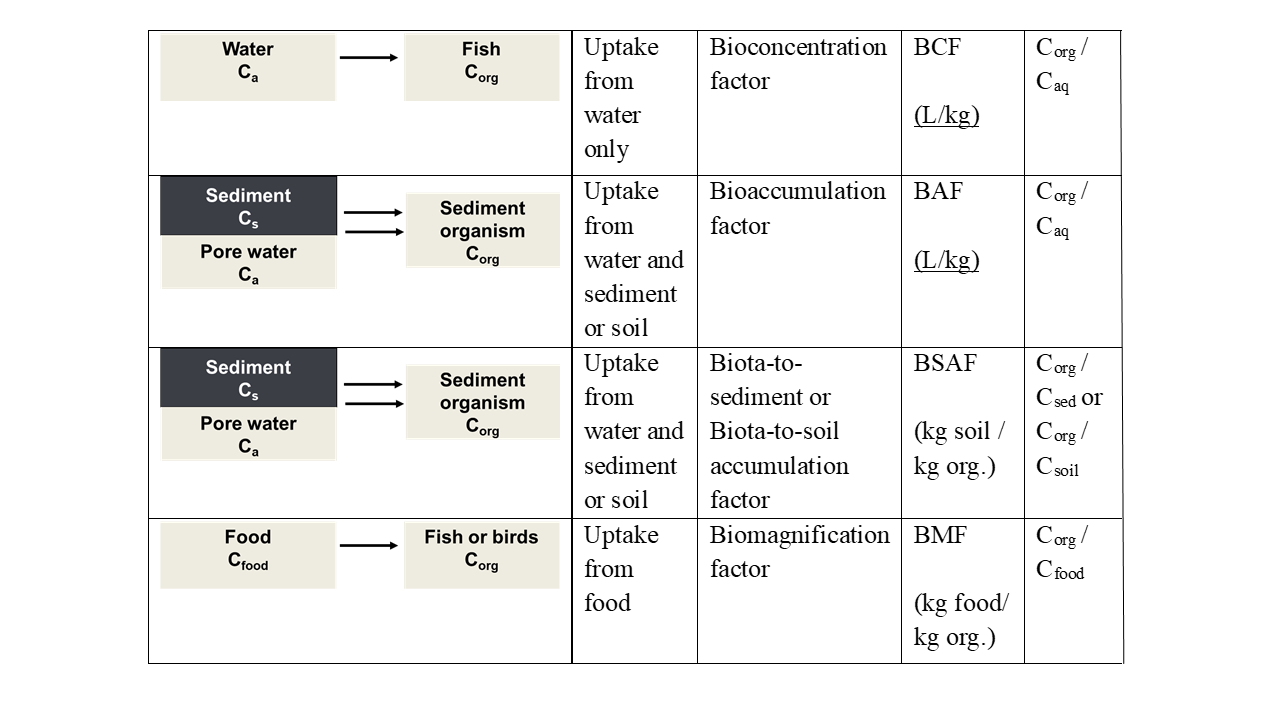
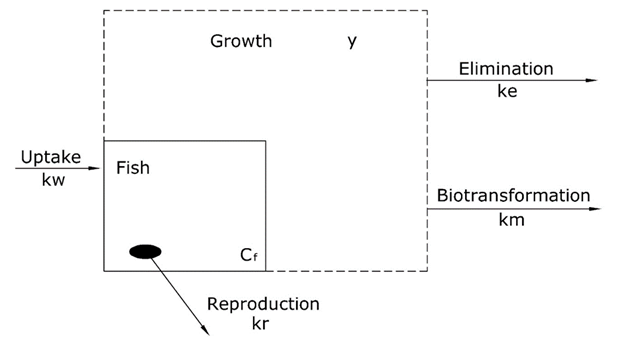
 Corg/Caq becomes constant. This is the steady state situation. The constant Corg/Caq at steady state is called the bioconcentration factor BCF. Mathematically, the BCF can also be calculated from
Corg/Caq becomes constant. This is the steady state situation. The constant Corg/Caq at steady state is called the bioconcentration factor BCF. Mathematically, the BCF can also be calculated from  kw/ke. This follows directly from equation 4: after long exposure time (t),
kw/ke. This follows directly from equation 4: after long exposure time (t),