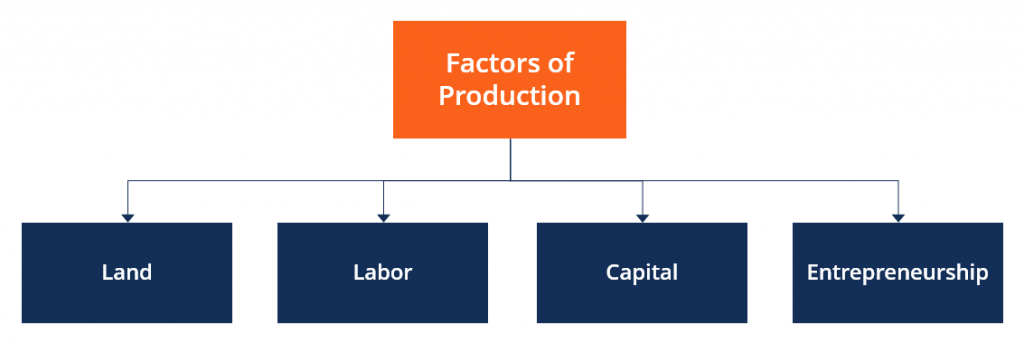
Het arrangement PROSPERITY is gemaakt met Wikiwijs van Kennisnet. Wikiwijs is hét onderwijsplatform waar je leermiddelen zoekt, maakt en deelt.
- Auteur
- Laatst gewijzigd
- 24-01-2024 14:28:36
- Licentie
-
Dit lesmateriaal is gepubliceerd onder de Creative Commons Naamsvermelding 4.0 Internationale licentie. Dit houdt in dat je onder de voorwaarde van naamsvermelding vrij bent om:
- het werk te delen - te kopiëren, te verspreiden en door te geven via elk medium of bestandsformaat
- het werk te bewerken - te remixen, te veranderen en afgeleide werken te maken
- voor alle doeleinden, inclusief commerciële doeleinden.
Meer informatie over de CC Naamsvermelding 4.0 Internationale licentie.
Aanvullende informatie over dit lesmateriaal
Van dit lesmateriaal is de volgende aanvullende informatie beschikbaar:
- Toelichting
- 10 Minutes Lesson
- Leerniveau
- VWO 3;
- Eindgebruiker
- leerling/student
- Moeilijkheidsgraad
- gemiddeld
Bronnen
| Bron | Type |
|---|---|
|
Prosperity https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lE9j87ERNxU |
Link |
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lE9j87ERNxU https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lE9j87ERNxU |
Video |
|
PowerPoint Mindmap Prosperity https://hrnl-my.sharepoint.com/:p:/g/personal/0981170_hr_nl/EZF7EaonypFKoZKaqFXk9h0BvtNfCZdxFaIwfsPNQJSdKQ?e=CmJKV5 |
Link |
|
https://academy.europa.eu/courses/discover-the-english-language-with-online-language-support/view?title=discover-the-english-language-with-online-language-support https://academy.europa.eu/courses/discover-the-english-language-with-online-language-support/view?title=discover-the-english-language-with-online-language-support |
Video |