Het arrangement Kennis van land en samenleving is gemaakt met Wikiwijs van Kennisnet. Wikiwijs is hét onderwijsplatform waar je leermiddelen zoekt, maakt en deelt.
- Auteurs
- Laatst gewijzigd
- 08-09-2021 09:13:26
- Licentie
-
Dit lesmateriaal is gepubliceerd onder de Creative Commons Naamsvermelding 4.0 Internationale licentie. Dit houdt in dat je onder de voorwaarde van naamsvermelding vrij bent om:
- het werk te delen - te kopiëren, te verspreiden en door te geven via elk medium of bestandsformaat
- het werk te bewerken - te remixen, te veranderen en afgeleide werken te maken
- voor alle doeleinden, inclusief commerciële doeleinden.
Meer informatie over de CC Naamsvermelding 4.0 Internationale licentie.
Aanvullende informatie over dit lesmateriaal
Van dit lesmateriaal is de volgende aanvullende informatie beschikbaar:
- Eindgebruiker
- leerling/student
- Moeilijkheidsgraad
- gemiddeld
Bronnen
| Bron | Type |
|---|---|
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q7Aq50-fuZg https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q7Aq50-fuZg |
Video |
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AM_kpc_WsFI https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AM_kpc_WsFI |
Video |
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_L5PR5TlTso https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_L5PR5TlTso |
Video |
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oemfO56t9yw&t=14s https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oemfO56t9yw&t=14s |
Video |
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H8uy86v6Kaw https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H8uy86v6Kaw |
Video |
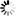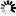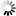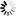


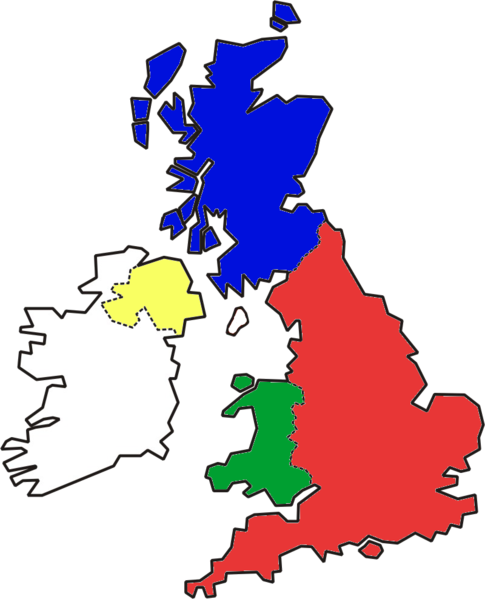


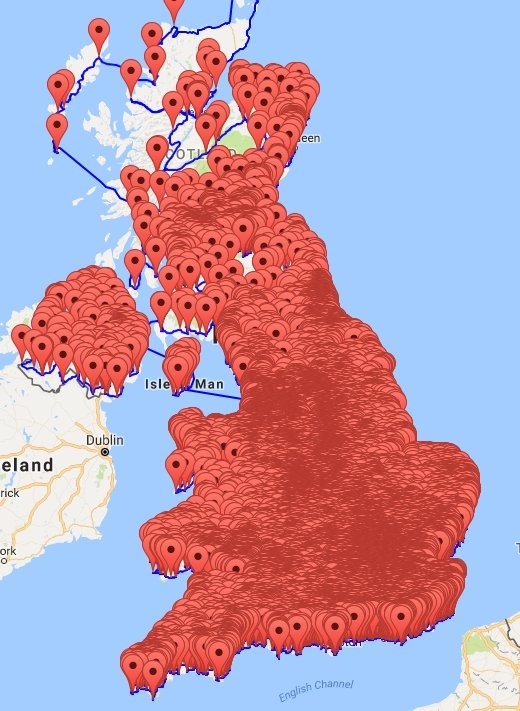
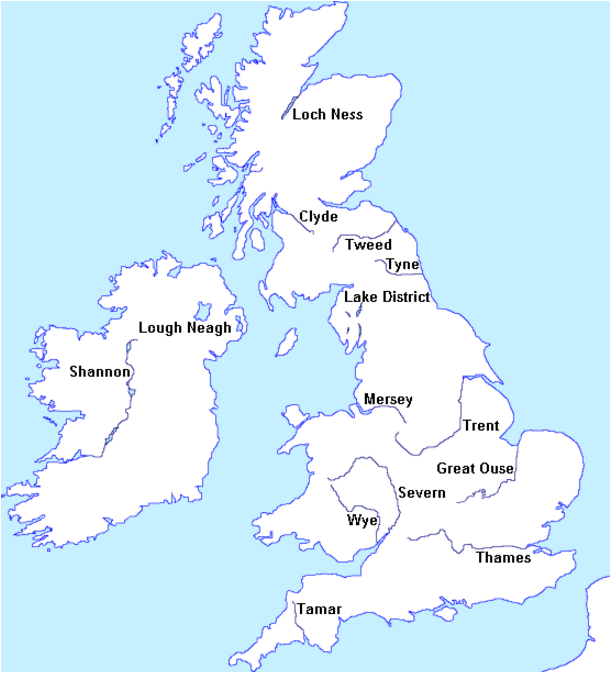
 Provide the same information from the cards for the Republic of Ireland. Again, mention at least two famous places and three famous attractions or sights per country.
Provide the same information from the cards for the Republic of Ireland. Again, mention at least two famous places and three famous attractions or sights per country.
 FAST FACTS
FAST FACTS
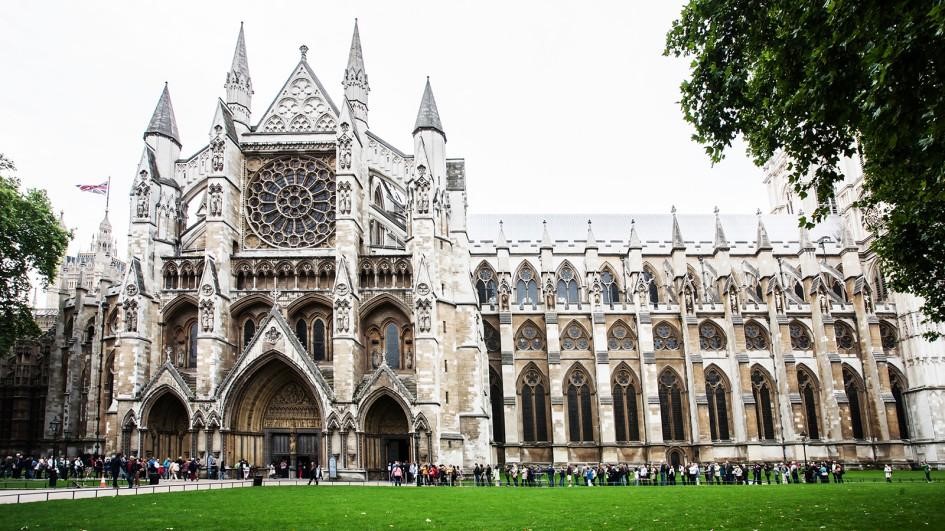
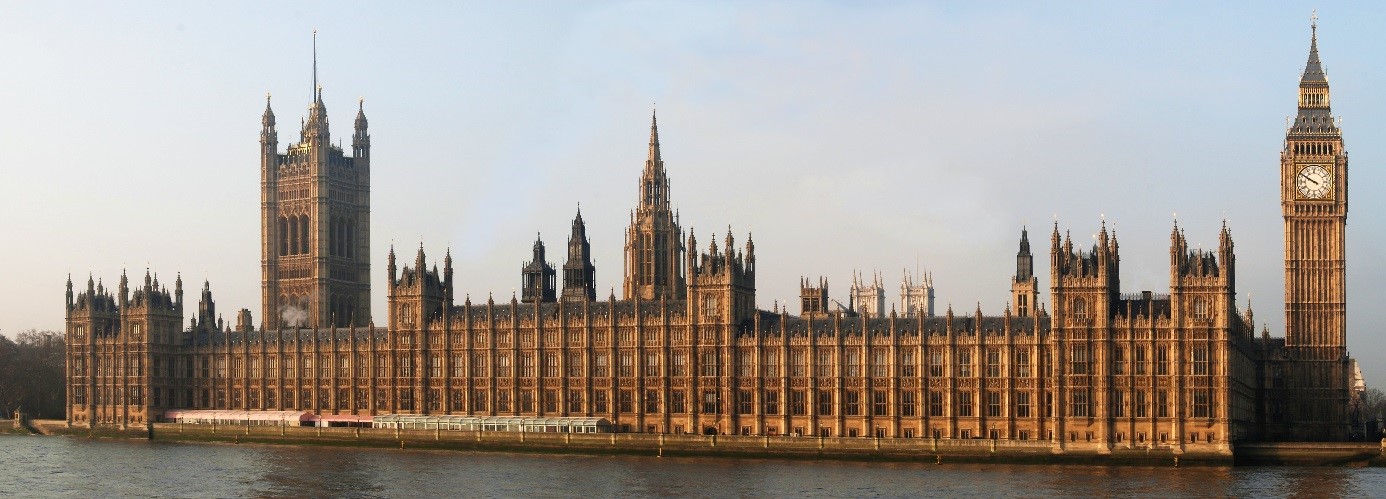
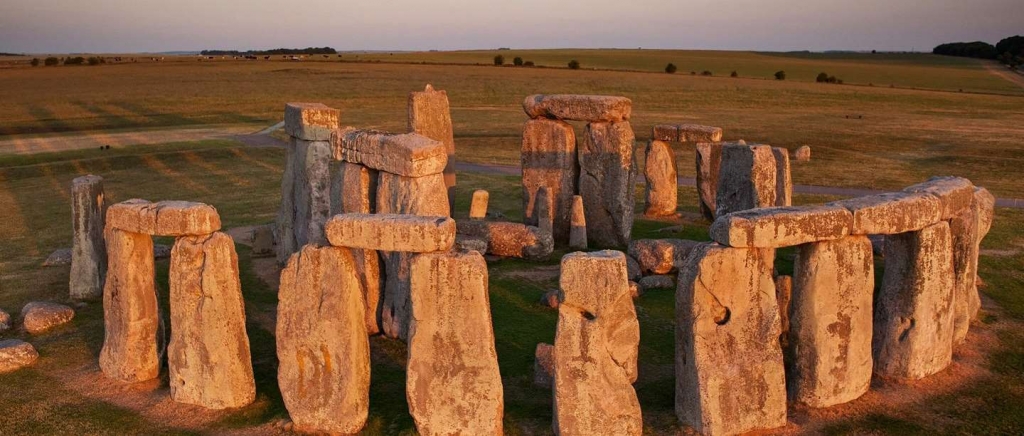
 CAPITAL: London
CAPITAL: London
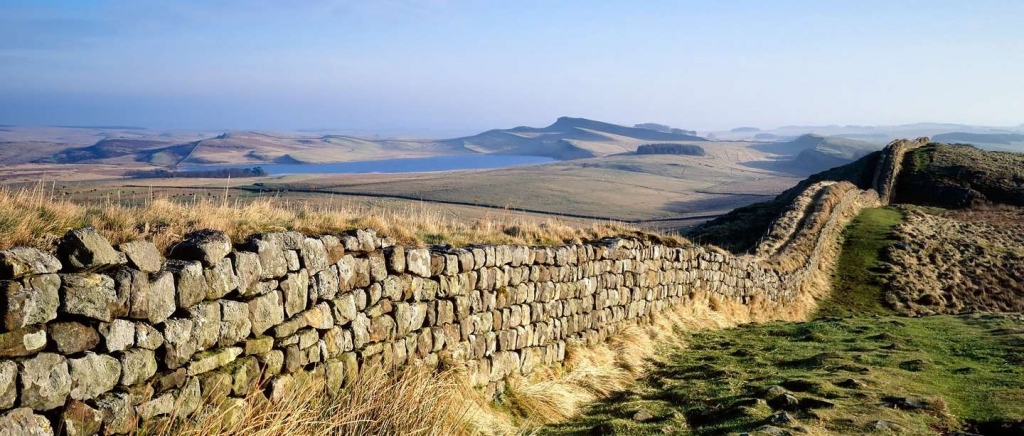










 After the collapse of the Roman Empire, during this period of recovery, several important ideas on how to keep things in control came up: feudalism, knighthood, and manorialism. Let’s break these down and try to understand what each involved. Feudalism was a system of governing people based on loyalty. This loyalty went upward, almost like a pyramid. The lower classes were loyal to the noble classes, the noble classes to the king, and the king was loyal to the teachings of Christianity.
After the collapse of the Roman Empire, during this period of recovery, several important ideas on how to keep things in control came up: feudalism, knighthood, and manorialism. Let’s break these down and try to understand what each involved. Feudalism was a system of governing people based on loyalty. This loyalty went upward, almost like a pyramid. The lower classes were loyal to the noble classes, the noble classes to the king, and the king was loyal to the teachings of Christianity. The High Middle Ages saw many changes: more food, more people, and more trade with other cultures than ever before. New areas of the world were being explored, and great explorers such as Marco Polo were making names for themselves. Europeans were divided into separately-ruled areas that we recognize today, such as Portugal, Spain, France, England, and Italy (along with other nation-states), but there was still warring over lands and territories. Feudalism was becoming a thing of the past, and people were moving toward a more city-focused lifestyle, with shops and shop-signs, markets and goods, and even guilds for learning new trades. Life was certainly very different than it had been in the Early Middle Ages.
The High Middle Ages saw many changes: more food, more people, and more trade with other cultures than ever before. New areas of the world were being explored, and great explorers such as Marco Polo were making names for themselves. Europeans were divided into separately-ruled areas that we recognize today, such as Portugal, Spain, France, England, and Italy (along with other nation-states), but there was still warring over lands and territories. Feudalism was becoming a thing of the past, and people were moving toward a more city-focused lifestyle, with shops and shop-signs, markets and goods, and even guilds for learning new trades. Life was certainly very different than it had been in the Early Middle Ages.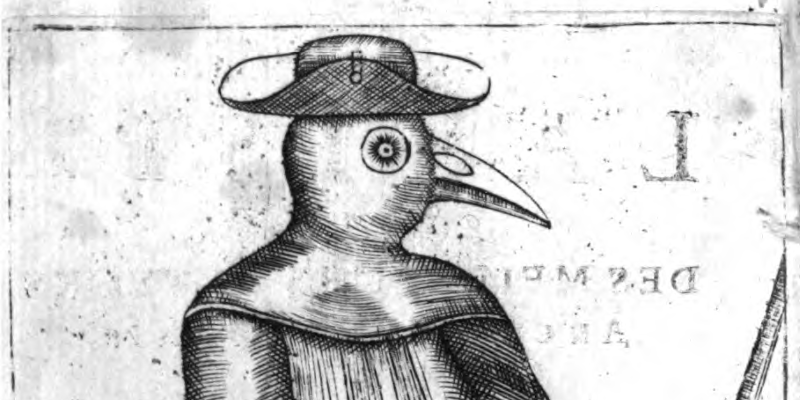 The Late Middle Ages saw everything grind to a long halt. We’ll talk about the many issues the people of this period faced, including famine, plague, crusades and wars over who should truly rule countries, but it’s always good to keep in mind that every period of history has its positives and negatives, and despite the challenges the people of the Late Middle Ages faced, the end result was a movement toward new thinking and the beginning of a period known as the Renaissance-the turning point of European history.
The Late Middle Ages saw everything grind to a long halt. We’ll talk about the many issues the people of this period faced, including famine, plague, crusades and wars over who should truly rule countries, but it’s always good to keep in mind that every period of history has its positives and negatives, and despite the challenges the people of the Late Middle Ages faced, the end result was a movement toward new thinking and the beginning of a period known as the Renaissance-the turning point of European history.







 Overall, however, the country was really seeing much more income in general. The vast majority of it was going to a small group who were becoming extremely wealthy. The downside is that many did not see such wealth because it was never passed down to the average workers. Still, England primarily views this as a time of prosperity despite the fact that the industrial revolution caused some growing pains within capitalism.
Overall, however, the country was really seeing much more income in general. The vast majority of it was going to a small group who were becoming extremely wealthy. The downside is that many did not see such wealth because it was never passed down to the average workers. Still, England primarily views this as a time of prosperity despite the fact that the industrial revolution caused some growing pains within capitalism.